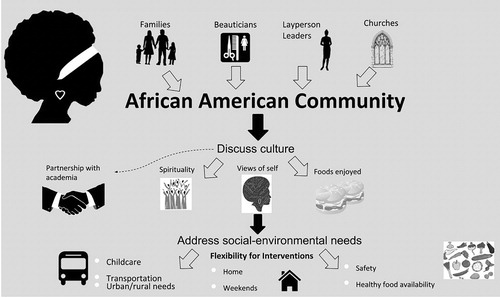
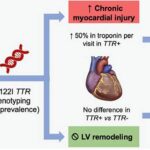
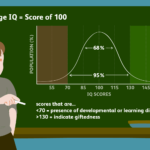
Health disparities among different racial and ethnic groups can be influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, social, and cultural factors. It’s important to note that generalizations about any racial or ethnic group can oversimplify the complex interplay of these factors. Nevertheless, some health conditions are known to disproportionately affect certain populations. It’s crucial to approach this topic with sensitivity and an understanding that individual health outcomes can vary widely within any racial or ethnic group.
Here are ten health conditions that have been observed to impact the black community at higher rates, influenced by a combination of genetic, cultural, and socio-economic factors:
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Hypertension is more prevalent among African Americans, and they tend to develop it at an earlier age compared to other ethnic groups.
- Type 2 Diabetes: African Americans are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Genetic factors, lifestyle, and socio-economic status contribute to this disparity.
- Obesity: Obesity rates are higher in the black community, and this can contribute to the prevalence of other health conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
- Cancer: Certain types of cancer, including breast, colorectal, and prostate cancer, disproportionately affect African Americans. Access to healthcare, genetics, and socio-economic factors contribute to these disparities.
- Sickle Cell Disease: Sickle cell disease is a genetic condition that predominantly affects people of African descent. It is more common among individuals with ancestors from regions where malaria is prevalent.
- Stroke: African Americans have higher rates of stroke, which can be attributed to hypertension, diabetes, and other risk factors.
- HIV/AIDS: HIV/AIDS disproportionately affects the black community, with higher rates of infection and a greater impact on health outcomes.
- Asthma: Asthma rates are higher among African Americans, and environmental factors, such as exposure to allergens and pollutants, can contribute to this disparity.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: African Americans have a higher risk of developing chronic kidney disease, often related to hypertension and diabetes.
- Maternal Mortality: Black women are at a higher risk of maternal mortality, reflecting disparities in healthcare access, quality, and socio-economic factors.
It’s crucial to approach discussions about health disparities with sensitivity and avoid reinforcing stereotypes. Addressing these disparities requires a multifaceted approach, including improved access to quality healthcare, addressing social determinants of health, and raising awareness about preventive measures within diverse communities.